HOW DOES THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM WORK?
Whenever there are deviations from homeostasis in the body’s functions, the endocannabinoid system is activated and begins to respond accordingly by synthesizing endocannabinoids, which act as neurotransmitters.
When the body creates endocannabinoid neurotransmitters, they are picked up by specialized cannabinoid receptors, which sit on the surface of cells. These receptors are found in a wide range of physiological regions, such as in:
- The immune system
- Organs and glands
- Connective tissue
- The brain (most significantly)
Like a key fits into a lock, endocannabinoids interact with these receptors and transmit information about changing conditions to kick-start a response, with the goal of helping the body achieve homeostasis, or equilibrium, within the body despite outside influences (Alger, 2013).
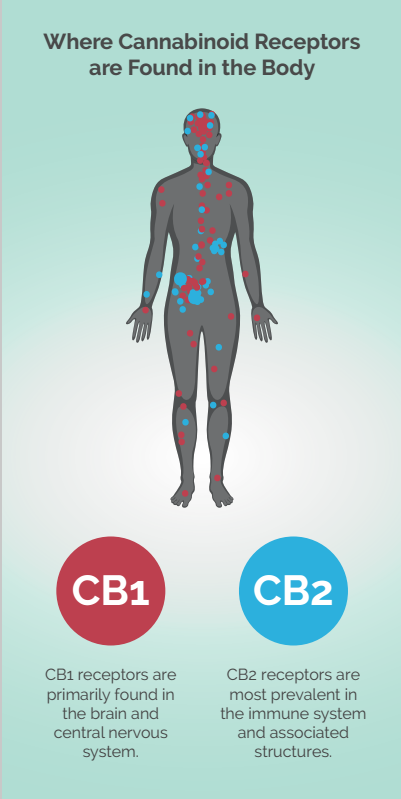
The endocannabinoid system’s receptor sites include CB1 and CB2 receptor variants, which respond differently to various cannabinoids (Pacher et al, 2006). CB1 receptors are most prevalent in the central nervous system and are linked to the following benefits:
- Modulation of stress and anxiety
- Increased appetite
- Decreased nausea
- Balance of immune system
- Inhibition of tumors
CB2 receptors are found mostly on cells in the immune system and seem to dominate in fighting inflammation and damage to tissue. Some cells can even contain both types of receptors, each responsible for a different function.
There are two major endocannabinoids – 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) and Anandamide (AEA).
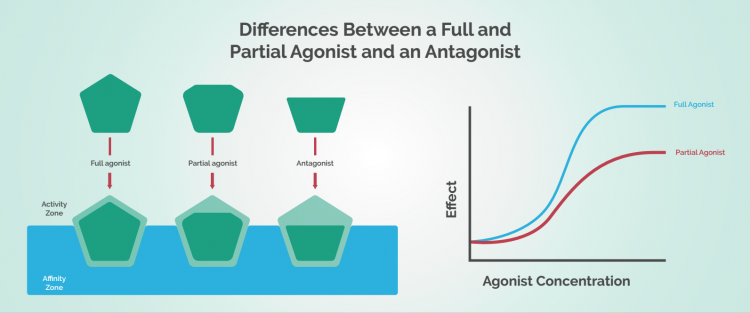
2-AG is considered a full agonist of both CB1 and CB2 receptors. This means that it binds with, and fits well inside, both receptors to activate them to stimulate a physiological response.
Anandamide is considered a partial agonist of both receptors, because, while it binds with and activates the receptors, it doesn’t fit as well inside them and subsequently doesn’t trigger such a powerful physiological response (Parcher, Batkai & Kunos, 2006).
Once the function that had deviated from homeostasis returns to equilibrium and the endocannabinoids are no longer needed, the third piece of the system – the metabolic enzymes – breaks down and degrades them.
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) degrades Anandamide, and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) breaks down 2-AG. By eliminating the endocannabinoids, the endocannabinoid system “turns off” the molecular signals and ends whatever physiological activity it had stimulated.
Send inquiry online For more product information and prices
(Pharmaceutical Ingredients Manufacturer & Supplier & Exporter.)
After sending the online inquiry, we will reply you as soon as possible, if not get any response on time please contact us by Tel or Email. —— Green Stone Swiss
Email: sales@raw-pharmaceutical-materials.comTel: +86 592 5365887
WhatsApp: +86 189 6515 7632
Send inquiry online:

